A new DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT is now available

Drug Trials Snapshots: NEXLETOL
NEXLETOL is a drug for the treatment of high LDL cholesterol, which is sometimes referred to as “bad cholesterol”.
NEXLETOL is to be used in the following two groups of patients: 1) patients with an inherited condition called heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) or 2) patients with complications from too much cholesterol (known as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease-ASCVD), such as heart attacks and strokes.
NEXLETOL is a tablet used once daily, in addition to low cholesterol diet and the highest dose of a statin (another drug commonly used to lower cholesterol) that a patient can tolerate. It should only be taken when LDL cholesterol needs to be lowered further.
See more Drug Trials Snapshots or contact us with questions at Snapshots@fda.hhs.gov.
NEXLETOL (bempedoic acid)
nex' leh tol
Esperion
Approval date: February 21, 2020
nex' leh tol
Esperion
Approval date: February 21, 2020
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
NEXLETOL is a drug for the treatment of high LDL cholesterol, which is sometimes referred to as “bad cholesterol”.
NEXLETOL is to be used in the following two groups of patients: 1) patients with an inherited condition called heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) or 2) patients with complications from too much cholesterol (known as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease-ASCVD), such as heart attacks and strokes.
How is this drug used?
NEXLETOL is a tablet used once daily, in addition to low cholesterol diet and the highest dose of a statin (another drug commonly used to lower cholesterol) that a patient can tolerate. It should only be taken when LDL cholesterol needs to be lowered further.
What are the benefits of this drug?
NEXLETOL lowers LDL cholesterol.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: NEXLETOL worked similarly in men and women.
- Race: NEXLETOL worked similarly in White and Black or African-American patients. The number of patients of other races was limited; therefore, differences in response for other races could not be determined.
- Age: NEXLETOL worked similarly in all age groups tested.
What are the possible side effects?
NEXLETOL may cause serious side effects including tendon rupture, and high uric acid levels in the blood.
The most common side effects of NEXLETOL are upper respiratory tract infection, increase in blood levels of uric acid, muscle cramps, back and extremity pain, stomach pain, bronchitis, anemia and elevated liver enzymes.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients in the trials were White. Differences in side effects among races could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of side effects was similar in patients younger and older than 65 of age.
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved NEXLETOL based on evidence from two clinical trials (Trial 1/ NCT02666664 and Trial 2/NCT02991118) of 3009 patients with high LDL cholesterol and known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease or HeFH. The trials were conducted in United States, Canada, and Europe.
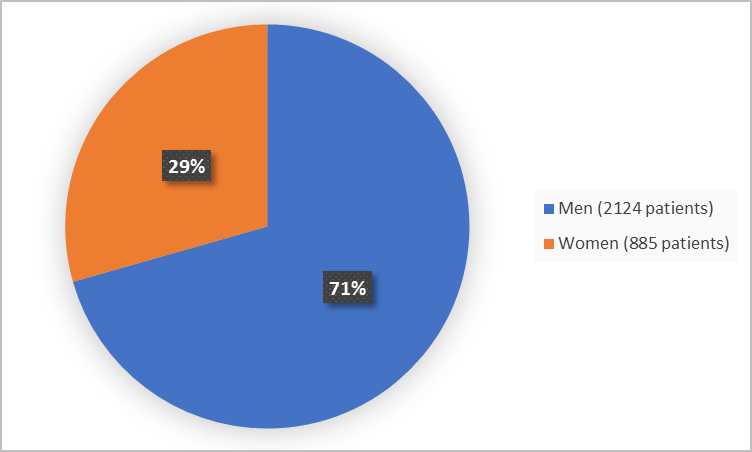
The figure below summarizes how many men and women were in these clinical trials.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex
Clinical Trial Data
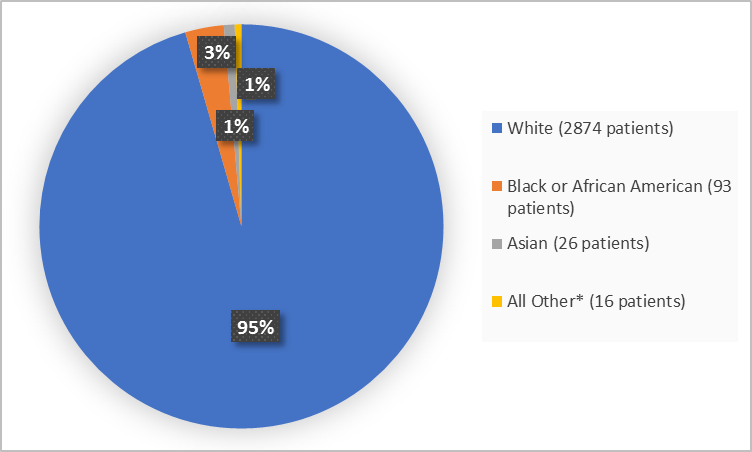
The figure summarizes the percentage of patients by race in these clinical trials.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race
*Includes American Indian or Alaska Native, Multiple, Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, and Other
Clinical Trial Data
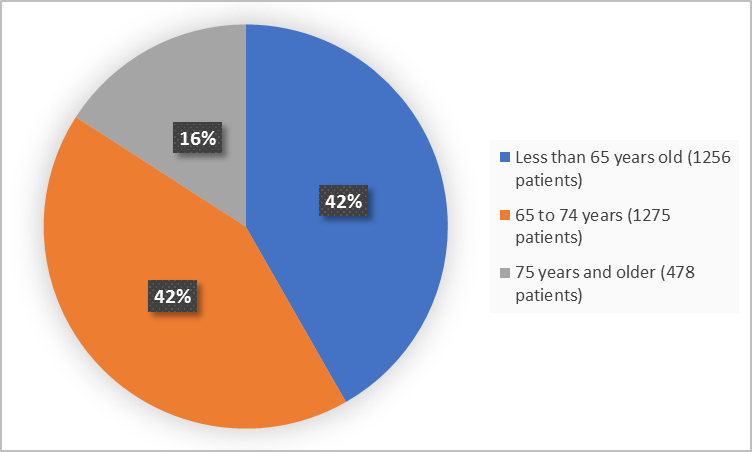
The figure below summarizes the percentage of patients by age in the clinical trials.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age
Clinical Trial Data
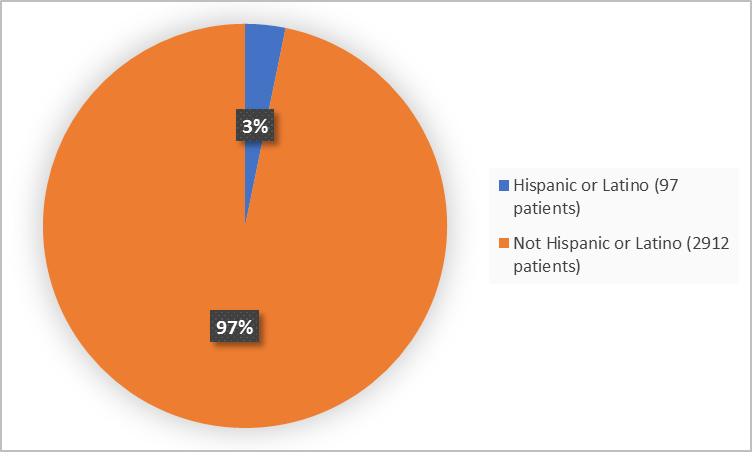
Figure 4. Baseline Demographics by Ethnicity
Clinical Trial Data
How were the trials designed?
There were two clinical trials that evaluated the benefits and side effects of NEXLETOL. The trial designs were similar.
All enrolled patients were on a low cholesterol diet and taking the highest dose of a statin (drug commonly used to lower cholesterol), for high cholesterol. In both trials, patients were randomly assigned to receive NEXLETOL or placebo tablets every day for 52-weeks. Neither the patients nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given.
The trials measured percent change in LDL-C blood levels from baseline to week 12 and compared NEXLETOL to placebo.
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
No comments:
Post a Comment