
A new DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT is now available.
XPOVIO is a drug used to treat a form of blood cancer called multiple myeloma. It is to be used in combination with dexamethasone (a type of corticosteroid) in patients with no other treatment options whose cancer came back after, or did not respond to, at least four previous treatments.
XPOVIO is a tablet. Four tablets (80mg) are taken by mouth in combination with dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week.
See more Drug Trials Snapshots or contact us with questions at Snapshots@fda.hhs.gov
XPOVIO (selinexor)
(x-PO-Vee-O)
Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc.
Approval date: July 3, 2019
(x-PO-Vee-O)
Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc.
Approval date: July 3, 2019
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
XPOVIO is a drug used to treat a form of blood cancer called multiple myeloma. It is to be used in combination with dexamethasone (a type of corticosteroid) in patients with no other treatment options whose cancer came back after, or did not respond to, at least four previous treatments.
How is this drug used?
XPOVIO is a tablet. Four tablets (80mg) are taken by mouth in combination with dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week. The XPOVIO dose may be decreased according to a special schedule if the patient cannot tolerate the side effects.
What are the benefits of this drug?
In the trial, 21 of 83 patients (25%) treated with XPOVIO in combination with dexamethasone experienced improvement in their disease that lasted about 4 months.
XPOVIO was approved under FDA’s accelerated approval program, which provides earlier patient access to a promising new drug while the company continues to conduct clinical trials to confirm that the drug works well.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
- Sex: XPOVIO was similarly effective in men and women.
- Race: The majority of patients were White. Differences in response to XPOVIO among different races could not be determined.
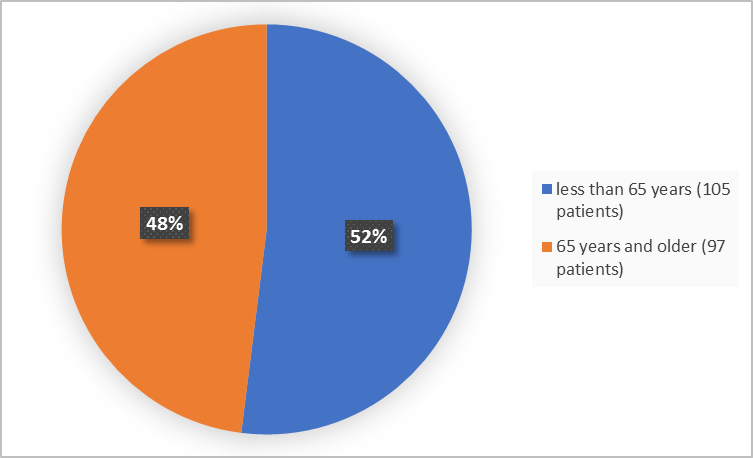
- Age: XPOVIO was similarly effective in patients below and above 65 years of age.
What are the possible side effects?
XPOVIO may cause serious reactions including low blood platelet count (thrombocytopenia), low neutrophil count (neutropenia), infections, gastrointestinal and nervous toxicity and low blood sodium.
The most common side effects of XPOVIO are low blood counts, nausea, fatigue, decreased appetite, decreased weight, diarrhea, vomiting, low blood sodium, constipation, shortness of breath, and upper respiratory tract infections.
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in men and women.
- Race: The occurrence of side effects between White and Black or African American patients was similar. Differences in side effects among other races could not be determined because of the small number of patients in those races.
- Age: The occurence of overall side effects was similar in patients below and above 65 years of age. Certain side effects—called serious adverse events1 --were seen more frequently in patients age 75 and above compared to those below the age of 75.
1 Serious adverse event is defined as any event that results in one of the following: death, life-threatening event, required hospitalization or extended a current hospital stay, persistent or significant disability/incapacity, or congenital anomaly or birth defect.
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved XPOVIO based on evidence from a clinical trial (NCT02336815) of 202 patients with multiple myeloma whose disease came back after, or did not respond to, previous treatments. The trial was conducted at 58 sites in US and Europe.
Presented below are all 202 patients who provided data for evaluation of side effects (called the safety population). Some of these patients (83) also provided data for evaluation of the benefits. Demographics of these patients are presented in Table 9 under MORE INFO.
Figure 1 summarizes how many men and women were in the clinical trial.
Figure 1. Baseline Demographics by Sex (safety population)
FDA Review
Figure 2 and Table 1 summarize the percentage of patients by race enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 2. Baseline Demographics by Race (safety population)
FDA Review
Table 1. Demographics of Efficacy Trials by Race
| Race | Number of Patients | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 148 | 73 |
| Black or African American | 35 | 17 |
| Asian | 2 | 1 |
| Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander | 1 | less than 1 |
| Other | 10 | 5 |
| Missing | 6 | 3 |
FDA Review
Figure 3 summarizes the percentage of patients by age group enrolled in the clinical trial.
Figure 3. Baseline Demographics by Age (safety population)
FDA Review
How were the trials designed?
All patients in the trial received XPOVIO in combination with dexamethasone twice a week until the disease progressed or the side effects became too toxic. The benefit of XPOVIO was measured by the proportion of patients that achieved improvement (overall response rate or ORR).
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.


No comments:
Post a Comment