
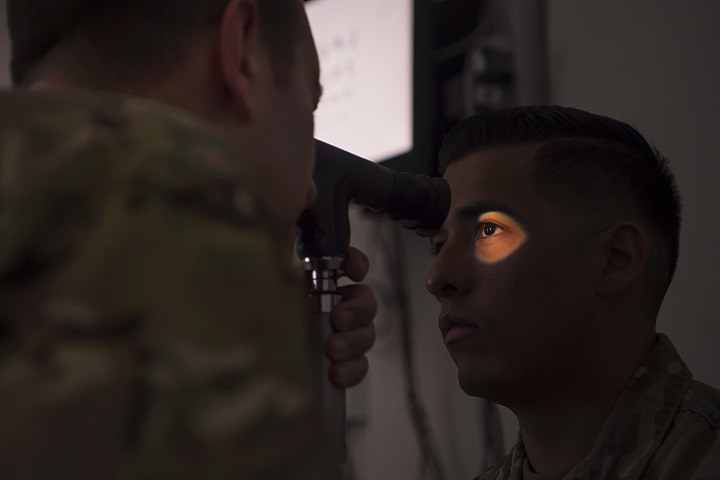
Dummies for doctors
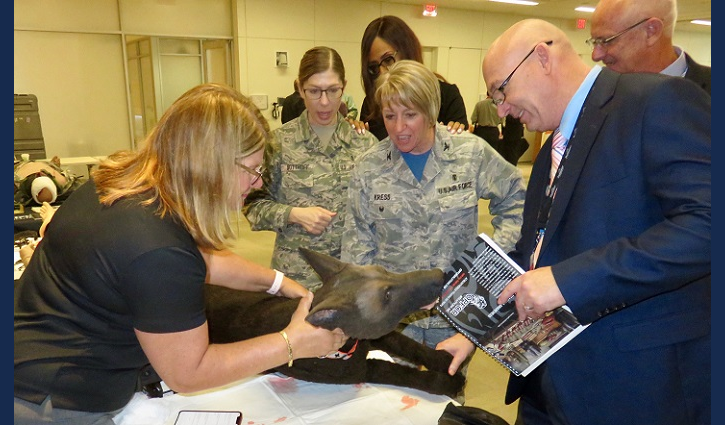

Air Force Col. Christine Kress (center) observes use of a medical canine mannequin designed to create training environments that prepare medical professionals for events they may face in the field. (MHS photo)
Artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR) are popular terms for computer-controlled technologies that can enhance our lives, but a new one, MMS, can help improve health care for patients within the Military Health System.
Medical modeling and simulation harnesses new technology to help train doctors, nurses, first responders, and other health care professionals by simulating realistic events in a training environment.
With a responsibility to improve delivery of health care to 9.5 million beneficiaries, the Defense Health Agency’s Medical Modernization and Simulation Division recently hosted its first Medical Modeling and Simulation Vendor Expo Day. There, vendors displayed their latest concepts for DHA decision makers.
“This is our first, and what I hope to be annual medical modeling and simulation expo to showcase our capabilities across the MHS,” said Air Force Col. Christine Kress, deputy assistant director, DHA Training and Education Directorate. “Our success relies on the partnerships we have with the industry in creating what we need to meet the training requirements of the warfighter.”
Those requirements include ensuring medical professionals are prepared for the scenarios they will face in the field, whether in a military treatment facility or on the battlefield.
“It all begins with training so that we can do the incredible things we do downrange,” Kress said.
“The Medical Modernization and Simulation Division is responsible for identifying and implementing the latest medical technology, data, research, procedures, and equipment utilized in the civilian sector or across our services,” said Army Master Sgt. Erik Z. McConnell, DHA’s senior enlisted adviser, Medical Modernization and Simulation Division, Education and Training Directorate.
Navy Hospital Corpsman 1st Class Alexis Sandoval, assigned to the U.S. Navy Bureau of Medicine and Surgery, cited the use of medical simulation mannequins on display at the Expo as great tools to help prepare corpsmen for the fleet.
“The technologies we see on display here would be very useful for us in the field. This technology would definitely help us improve our capabilities and save lives.” Sandoval said.
Sandoval also explained that in the past, the mannequins could only be used to simulate one medical condition, usually through application of moulage or other techniques. But with the development of more sophisticated medical simulation mannequins, instructors can now remotely make inputs that require trainees to reassess the patient and respond to rapidly changing medical conditions.
Medical technology, including medical simulation mannequins, has improved dramatically over the last few years, Sandoval said. “We are using technology more now than in the past to train corpsmen,” he added. “I like that! It exposes us to conditions we may have never seen before.”
DHA plans to provide more opportunities to showcase emerging medical technology at events like the modeling and simulation expo.
“We’re excited for the creation of new capabilities that we need to ensure our soldiers, sailors, and airmen are ready to go downrange and do the hard work that they do in saving lives,” Kress said.
Smartphone Apps for Psychological Health: A Brief State of the Science Review
Publication
5/14/2019
In this brief state of the science review, we provide a synopsis of the literature on psychological health mobile applications (apps) and discuss the impact of mobile technology on psychological health practice. We describe the variety of psychological health app uses from self-management, skills training, and supportive care to symptom tracking and data collection; and we summarize the current evidence for the efficacy and effectiveness of psychological health apps. Finally, we offer some pragmatic suggestions for evaluating psychological health apps for quality and clinical utility.
Cultural Considerations in Using Mobile Health in Clinical Care With Military and Veteran Populations
Publication
5/14/2019
Traditional cultural models typically address factors like ethnicity, language, and race as important concerns pertaining to treatment efficacy, but over the years, professionals have expanded the focus to include gender, sexual orientation, age, socioeconomic status, and other aspects of identity and experience, including military cultural issues. As the integration of mobile health increases in clinical care, another important cultural factor that can impact care is technological culture. Differences in perception of technological competence by patient and provider can impact the provider’s ability to effectively connect with the patient and fully leverage tools to support evidence-based treatment.
Mobile Applications for Client Use: Ethical and Legal Considerations
Publication
5/14/2019
Mobile applications (apps) to support behavioral health are increasing in number and are recommended frequently by medical providers in a variety of settings. As with the use of any adjunct tool in therapy, psychologists adopting new technologies in clinical practice must comply with relevant professional ethics codes and legal standards. However, emerging technologies can outpace regulations regarding their use, presenting novel ethical considerations. Therefore, it is incumbent upon providers to extrapolate current ethical standards and laws to new technologies before they recommend them as adjuncts to face-to-face treatment. This article identifies best practices for incorporating apps into treatment, including competence in the use of smartphones in general and familiarity with the specific apps recommended.
Military to bring eye care to front lines with mobile app
Article
4/11/2019
Air Force and Army medical researchers are developing a smart phone application to connect providers downrange with on-call ophthalmologists either in-theater or at a clinic
Military Health System Data Repository (MDR)
Fact Sheet
4/5/2019
The MDR is the centralized data repository that captures, archives, validates, integrates and distributes Defense Health Agency (DHA) corporate health care data worldwide.
Defense Occupational and Environmental Health Readiness System – Industrial Hygiene (DOEHRS-IH)
Fact Sheet
4/5/2019
DOEHRS-IH allows the Department of Defense (DoD) to manage occupational and environmental health risk data and actively track biological, chemical, physical health hazards and engineered nano-object process to service members worldwide.
Military Health System Management Analysis and Reporting Tool (M2)
Fact Sheet
4/5/2019
M2 is a powerful ad-hoc query tool used to manage and oversee operations worldwide.
TOL Patient Portal Secure Messaging
Fact Sheet
4/5/2019
TRICARE Online Patient Portal (TOLPP) Secure Messaging (SM) provides Military Health System patients who receive care at a military treatment facility or clinic access to a robust messaging capability, allowing authorized patients the ability to securely communicate with their health care team.
Defense Medical Human Resources System – internet (DMHRSi)
Fact Sheet
4/4/2019
DMHRSi manages human resources for the Defense Health Agency. It is the only Integrated Human Resource System within the Department of Defense.
Airmen perform in-flight Transportation Isolation System training
Article
3/14/2019
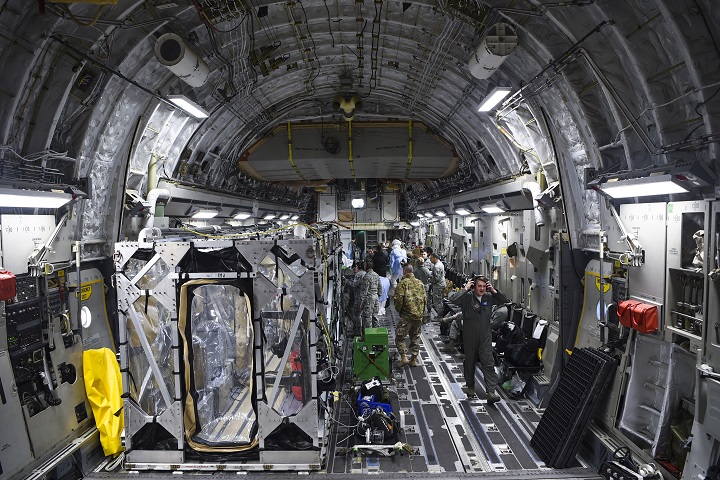

This mission capability is the only one of its kind in the Department of Defense
Composite Health Care System (CHCS)
Fact Sheet
3/14/2019
The Composite Health Care System (CHCS) allows clinicians to electronically perform patient appointment processes and scheduling, order laboratory tests, authorize radiology procedures and prescribe medications.
Centralized Credentials Quality Assurance System (CCQAS)
Fact Sheet
3/14/2019
Centralized Credentials Quality Assurance System (CCQAS) is a web-based worldwide credentialing, privileging, risk management and adverse actions application that supports more than 105,000 professionals providing health and wellness services to active duty military personnel, their families and selected retirees.
Coding and Compliance Editor (CCE)
Fact Sheet
3/13/2019
CCE supports the Department of Defense efforts to improve coding accuracy and reimbursements for inpatient and outpatient services.
Mobile app aids ‘truly informed’ contraception conversations between patients, providers
Article
3/11/2019
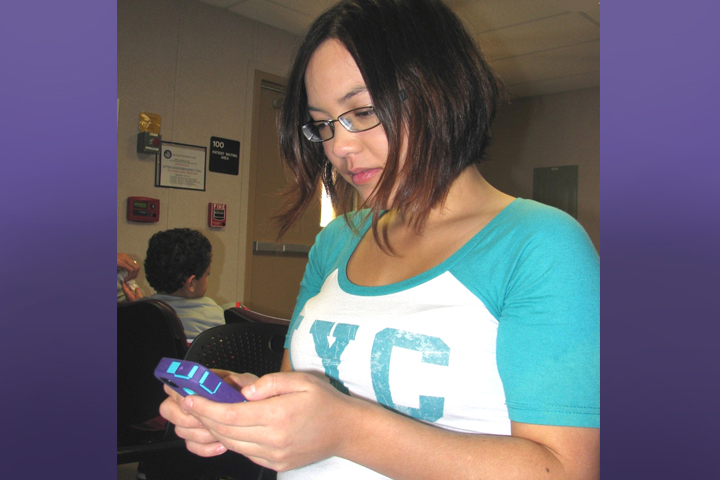

Decide + Be Ready, an app that provides information on contraception for men and women, is designed to help patients make informed decisions with their providers. The app also includes a module to address the unique needs of service women around deployment and duties.
Gone in a flash: ‘Floaters’ in field of vision can warn of vision issue
Article
2/14/2019

Jane Acton was familiar with vision issues and her quick action after experiencing the onset of retinal detachment was vital in recovering her vision
No comments:
Post a Comment